Single Cell Genome Sequencing Is A Technique That Allows Scientists To Analyze The Genetic Material
 |
| Single Cell Genome Sequencing |
Single Cell Genome Sequencing is a revolutionary technique that allows
scientists to analyze the genetic material of individual cells. Unlike
traditional genome sequencing methods, which require a large number of cells,
single-cell sequencing provides insights into the genomic heterogeneity and
diversity present within complex biological systems. The human body is composed of
trillions of cells, each with its own unique genetic makeup. Traditional
sequencing methods, such as bulk sequencing, average the genetic information of
all the cells in a sample, masking the genetic variations that may exist among
individual cells. Single-cell genome sequencing overcomes this limitation by
isolating and sequencing the DNA of individual cells, providing a detailed
understanding of cellular diversity.
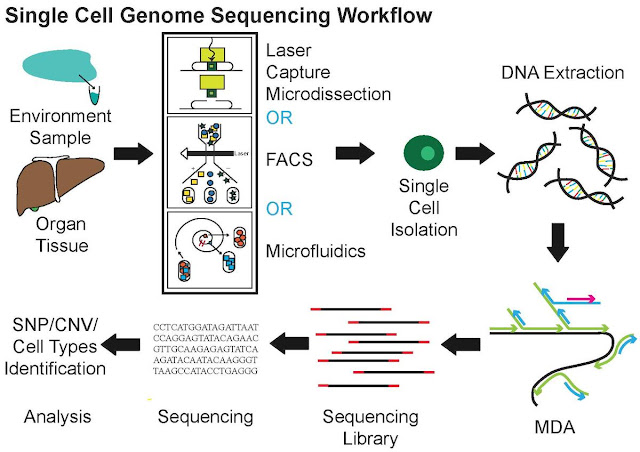
The process of Single Cell Genome
Sequencing involves
several key steps. First, individual cells are isolated using microfluidics or
manual techniques, ensuring that each cell is captured separately. Next, the
genomic DNA is extracted from each isolated cell. Due to the small amount of
DNA present in a single cell, amplification techniques, such as whole genome
amplification (WGA), are employed to increase the amount of DNA available for
sequencing. Once
the DNA is amplified, it can be sequenced using various techniques, such as
next-generation sequencing (NGS). NGS platforms generate vast amounts of
sequencing data, which is then processed and analyzed using bioinformatics
tools. These tools help identify genetic variations, mutations, and gene
expression profiles specific to individual cells. The resulting data provide
valuable insights into cellular heterogeneity, developmental processes, disease
progression, and more.
Single Cell Genome Sequencing has revolutionized various fields of research.
In the field of cancer biology, for example, it enables the identification of
rare subpopulations of cells within tumors that may drive resistance to therapies.
It also provides a deeper understanding of clonal evolution and the genomic
changes that occur during cancer progression. Furthermore, single-cell genome sequencing has proven
valuable in developmental biology, allowing researchers to study the gene
expression dynamics and lineage relationships of individual cells during
embryonic development. It has also shed light on the mechanisms underlying
tissue regeneration and neurodevelopmental disorders.
In addition to human health, Single Cell Genome Sequencing has been applied to other areas such
as microbial ecology and environmental studies. By sequencing individual
microbial cells, researchers can explore the diversity and functional potential
of microbial communities, contributing to our understanding of ecosystems and
their impact on the environment. Despite its numerous advantages, these are still faces
certain challenges. One of the main challenges is the technical difficulty and
cost associated with isolating and amplifying DNA from single cells.


Comments
Post a Comment